What is Industry 4.0?
The Mechanical Era
The First Industrial Revolution began at the end of the 18th century with the invention of the steam engine by James Watt in 1769, for which he filed a patent that would revolutionize the world. This innovation transformed craft workshops into mechanized factories. Production then became mechanical, marking the beginning of small-scale industrial series.
The Electrical Era
The Second Industrial Revolution was based on the use of electricity and oil. Over time, machines became increasingly efficient. This was the era of Taylorism and mass production. With electrification, assembly line work emerged, significantly increasing productivity.
The Automation Era
The rise of computing marked the Third Industrial Revolution. The automation of production lines became possible thanks to programmable robots. This was also the era of telecommunications and industrial flexibility. The Lean Manufacturing model, initiated by Toyota, put an end to Taylorism by promoting continuous improvement.
Industry 4.0: The Digitalization Era
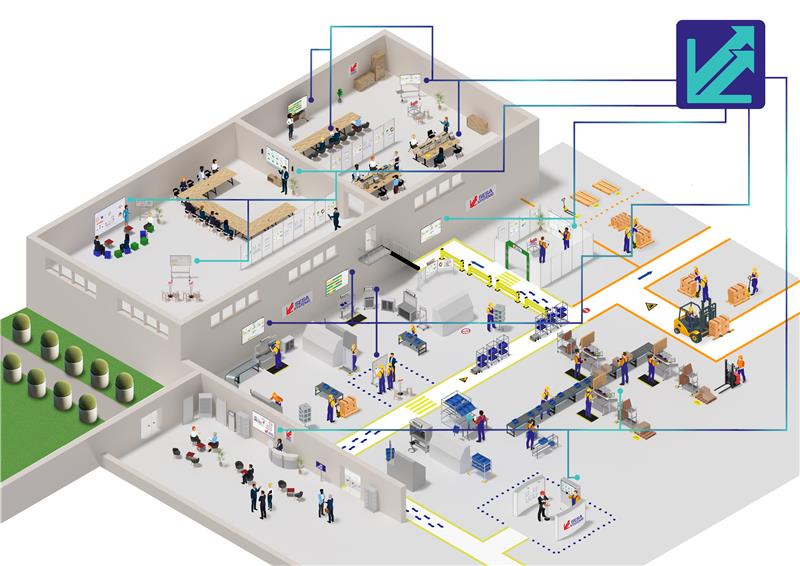
The fourth and latest industrial revolution to date emerged in 2011. Industry 4.0 integrates technological and digital objects into factories to optimize business activities. Production methods have become more intelligent, as all objects, machines, and operators in the value chain are interconnected. To achieve this, Industry 4.0 relies on eight key technologies.
Industry 5.0: The Era of Artificial Intelligence
The Fifth Industrial Revolution marks the beginning of a new era focused on the collaboration between humans and machines. Industry 5.0 aims to integrate advanced technologies while placing humans at the center of the production process. Unlike the extensive automation of Industry 4.0, this revolution focuses on co-creation and harmonious interaction between human operators and intelligent machines. This enhances performance while valuing human skills. To achieve these goals, Industry 5.0 relies on artificial intelligence (AI), collaborative robotics, and immersive technologies such as augmented reality.
IOT - The Internet of Things
The term "Internet of Things" refers to the embodiment of the internet in the real world. It includes all objects, such as vehicles, buildings, and others, as long as they are connected to an internet network. This means that an electronic chip, sensor, or any other form of connectivity must be present for the objects to be connected and able to communicate with each other, collect, and exchange information. IoT thus allows remote control and monitoring of objects.
CPS - Cyber-Physical Systems
A cyber-physical system is a system that autonomously exchanges information, controls processes, and triggers actions based on "circumstances". This is done using physical sensors that send information to a decision server, which in turn triggers an action. This system forms a decision loop that can continuously act on its environment.
Twin models - Digital Twin
According to Raksmey Han, a digital twin is usually a 3D model of a process, product, or service. It is a duplicate modeled using sensors on the main object to retrieve data. With this, it is possible to know the position of the object in space, its state, temperature, etc.
3D Printers
Additive manufacturing or 2D printing is a tool that creates physical objects layer by layer, through successive addition of material. Through Industry 4.0, 3D printing allows for rapid production of unique and customized products at low costs.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the protection of systems connected to the internet against cyber threats targeting hardware, software, and data. As Industry 4.0 develops the Internet of Things, it is crucial to protect the IT infrastructure from data breaches and the risk of remote control of the production tool, thus securing your domains.
Cobot - The Collaborative Robot
Cobots are collaborative robots implemented in industrial production plants. This means that robots work alongside the operator. Indeed, the cobot becomes a colleague to assist the operator in their daily tasks. These robots are safe and assist the operator in their most tedious or repetitive tasks.
Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a shared, on-demand network that provides access to computing services and resources such as servers, databases, storage, or software over the internet, aiming to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
AR - Augmented Reality
This technology integrates 3D virtual elements within a real environment. The principle is simple: it's the combination of the virtual and real to quickly obtain information for all collaborators. As a result, augmented reality increases the efficiency of the collaborator, just like cobots.